Voice disorders such as hoarseness, improper pitch etc. usually occur at the vocal cord level. Any vocal cord lesions such as polyps, nodules, cyst, sulci, may cause change in voice. Some of these conditions require surgery for correction. Voice surgery is done using microsurgery and requires extreme precision. We perform voice surgery using CO2 and diode laser. Following voice surgery, patient needs around 3 days of voice rest after which he can start using his voice normally.
Laser is a precision instrument that enables bloodless surgery with minimal collateral damage. The acronym LASER stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.” It uses a laser light source (laser beam) to remove diseased tissues.
There are various types of lasers used for performing surgeries like CO2, Argon, Nd-Yag, KTP, Dye Lasers and Diode laser. Voice preservation is optimal with the CO2 laser. The newer CO2 laser with higher modifications (Ultrapulse) have added more precision and improved outcomes. Laser phonosurgery and surgery for vocal cord malignancies give excellent results.
Microlaryngoscopy is a procedure that means the vocal folds are looked at in great detail with magnification. The magnification may be with a microscope. It is often accompanied by some additional procedure such as removal of a mass, swelling or tumor in larynx (voice box). Long delicate instruments or a laser may be utilized. It is more typically performed in the operating room.
Cyst / Polyp / Nodules are thickenings or callouses that form on the vocal folds. They occur because of repetitive and prolonged speech, excessive shouting and incorrect use of voice.
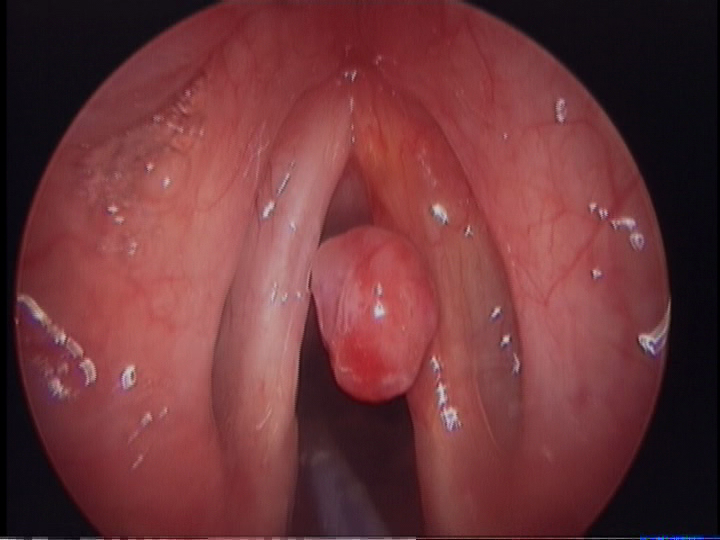

Granulomatous / Malignant lesions are non self-limiting growth that are capable of invading into adjacent tissues of the voice box.
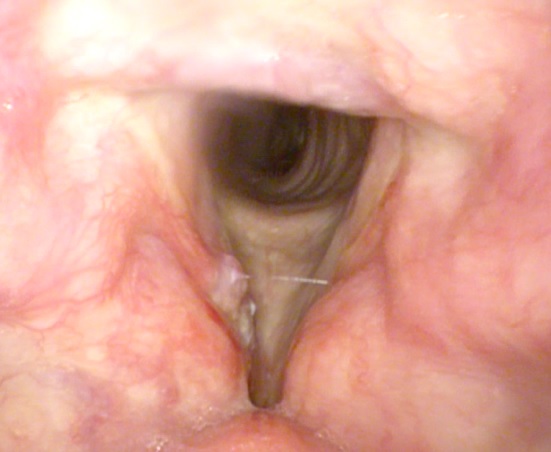
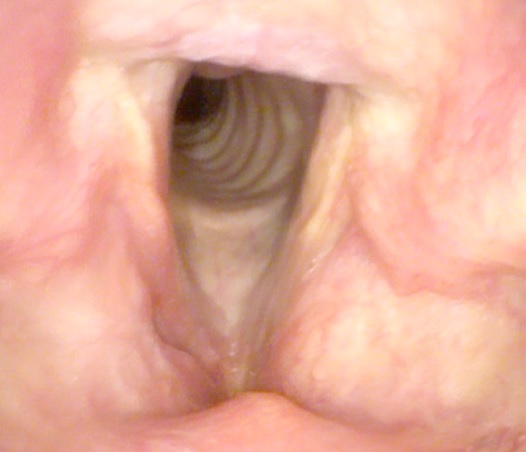
Laryngeal Papillomas are self-limiting mulberry or cauliflower like surface which appear in both children and adults.
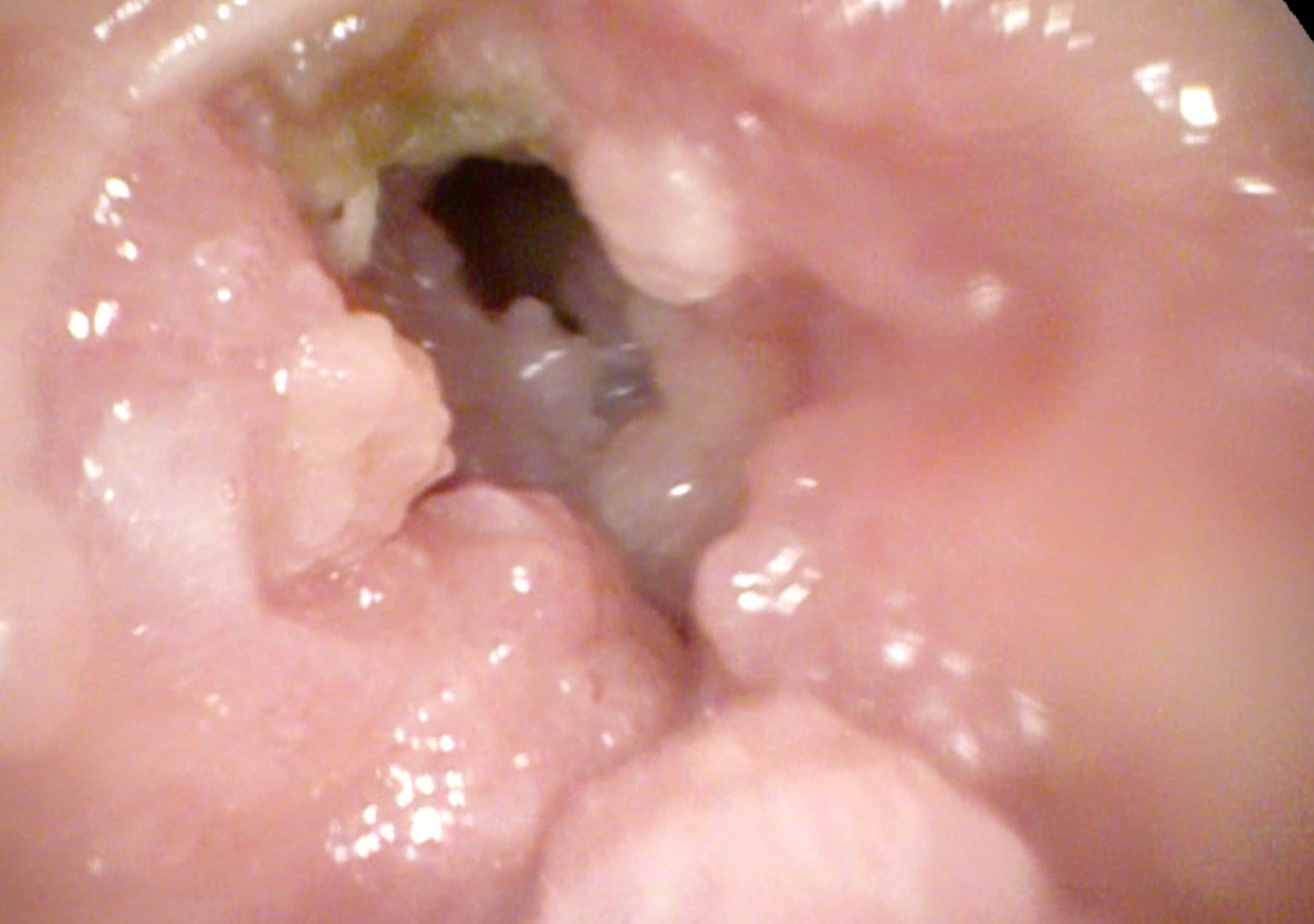

CO2 laser assisted M.L. scopy helps in exposure, magnification and precise excision of the above type of lesions. The result in the immediate post-operative period is generally good, the vocal fold quickly resumes its normal mass, and patients tend to have early return to normal voice.
This procedure is done in patients suffering from Bilateral Abductor cord Palsy i.e. both the vocal cord’s mobility is restricted such that they are unable to open for adequate passage of air into the air pipe. In such case, a small portion of the arytenoid and adjacent vocal cord is removed using laser. This results in adequate space for air to pass into the windpipe without disturbing the speech quality of the patient.
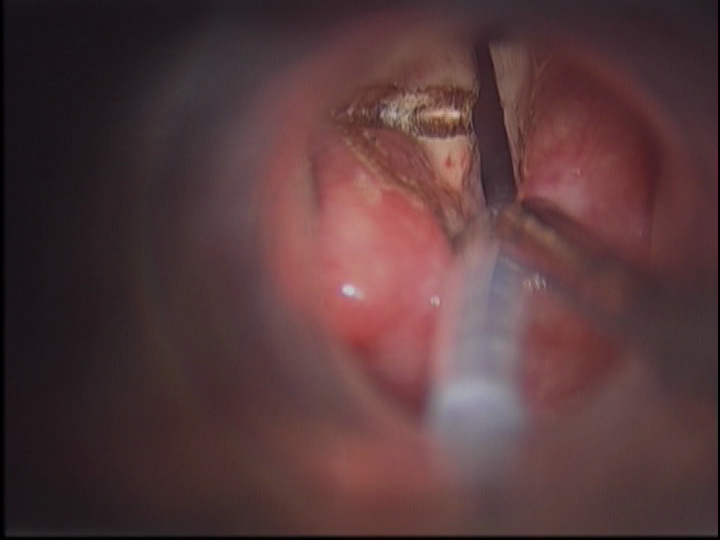
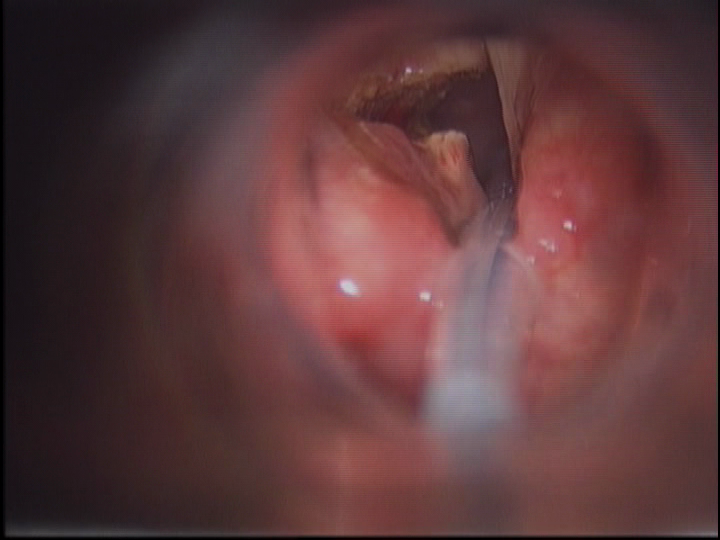

Glottic Web is a tissue or membrane over the voice box which may interfere with the normal voice or breathing. This glottic web is similar to the web one sees between adjacent fingers. Normally, in the absence of a glottic web, the mucosa covers each vocal cord individually to form a crisp “V”. It may be congenital (by birth) or may have occurred in an adult due to certain injury or trauma to the voice box. This surgery is performed under general anesthesia and proper ventilation. The web is incised with the CO2 laser and a keel is placed to prevent further web formation.
Spasmodic dysphonia (SD) remains one of the most difficult of laryngeal pathologies to treat. In laserThyro-arytenoid Myoneurectomy is done for the treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia, in which the patient has speech difficulty. The patient experiences difficulty in speech due to pitch breaks and spasms in the thyro arytenoid muscle of the larynx. The thyro arytenoid muscle fibers are destroyedendoscopically with the help of a CO2 laser. The branch of the nerve that supply the thyroarytenoid muscle is also looked for which is referred to as “fishing for the nerve” which shows significant long-term improvement in voice quality in terms of reduced speech brakes, effort and strain in voice.
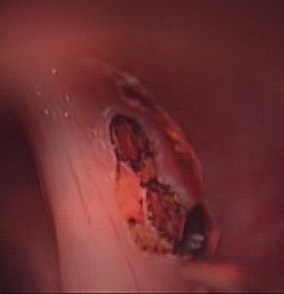
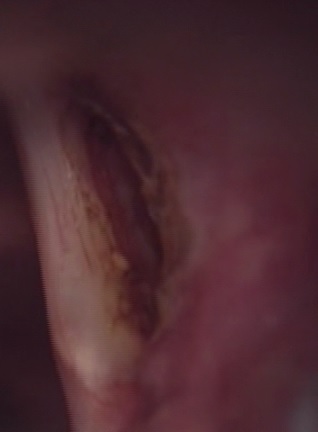
This procedure is used to visualize and biopsy diseases in and around the larynx. This is done with the help of a laryngoscope introduced in the patient’s mouth and fixed over the chest of the patient. The procedure requires general anesthesia.
The patient is positioned in a way that allows extension of the head and neck. The teeth and gums are protected, and the laryngoscope is introduced into the mouth and throat. The laryngoscope has a rigid, hollow barrel that allows one to visualize the larynx and pharynx. Endoscope is used for visualization and fiberoptic light cables are used for illumination. The operative microscope and lasers are also used when indicated.
Gap between the two vocal folds may be caused by vocal fold scars, sulci, single cord palsy or may be due to age (Presbylarnx). Vocal fold augmentation is a commonly used surgical treatment for glottic insufficiency. Varieties of injectable substances are available for vocal fold augmentation. Autologous fat is long-lasting injection, injected into the vocal folds, resulting in bulging of the cords thus reducing the vocal cord gap and improving the voice quality of the patient.
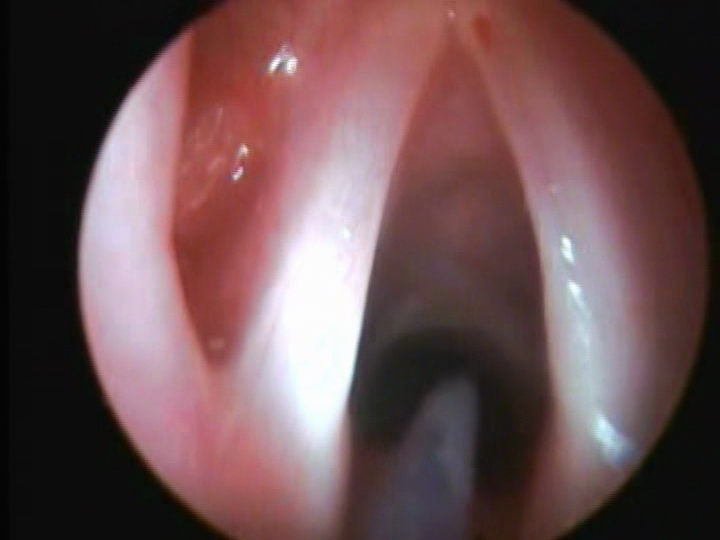

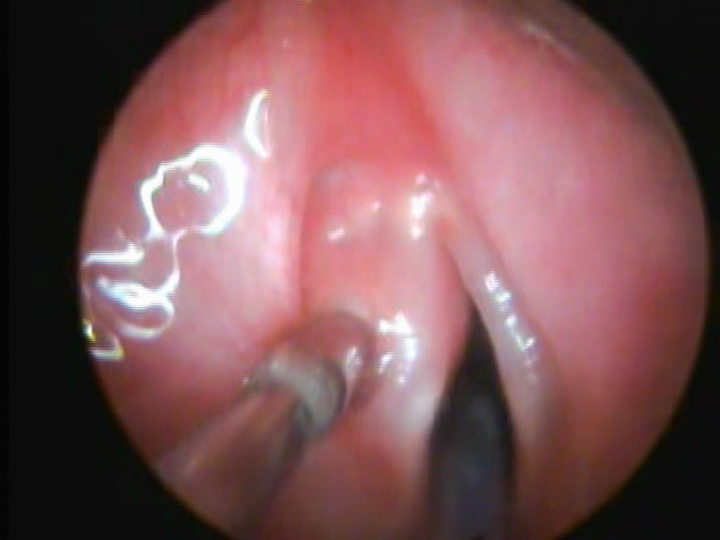

Laryngeal framework surgery involves changes to the “cartilage framework” of the larynx (voice box). The intent is to improve the position and/or contour of one or both vocal folds so they close better in order to vibrate better during speaking or singing – but without hindering passage of air for breathing. Common conditions where such surgeries are performed- young male having high –pitched or feminine voice, transgender surgeries, and single vocal cord paralysis.